Toxoplasmosis Information
Click here to scroll to the list of available medications ↓
60 million Americans are infected with toxoplasmosis annually, an infection caused by the parasite, Toxoplasma gondii. Toxoplasmosis is actually one of the most common infections caused by a parasite in the world. The majority of victims of toxoplasmosis never develop any symptoms as the body’s healthy immune system can often ward off the infection before it causes any signs of inhabitation. However, children, people with serious diseases, and patients infected with the HIV virus can be seriously compromised by the toxoplasmosis infection.
For those who develop symptoms, most patients experience fatigue, fever, body aches, swollen lymph nodes, and sometimes a sore throat. In many cases the symptoms are mild and disappear after a few days. Patients receiving chemotherapy, living with HIV or AIDS, and those who are otherwise jeopardized due to an unhealthy immune system are likely to experience more serious symptoms such as confusion, loss of coordination, headaches, seizures, severe inflammation of the retinas, and lung problems which mimic tuberculosis or other serious lung diseases.
Babies can be born to mothers who have had toxoplasmosis during pregnancy but never developed any symptoms. Newborns born with toxoplasmosis may experience symptoms such as an unusually large head from the accumulation of fluid, jaundice, severe eye infections, an enlarged liver, or an enlarged spleen. In some cases, babies don’t develop any symptoms until they have grown into their 20s or 30s, and then may experience symptoms such as hearing loss or significant hearing impairment, eye infections that may lead to blindness or visual impairment, and mental retardation.
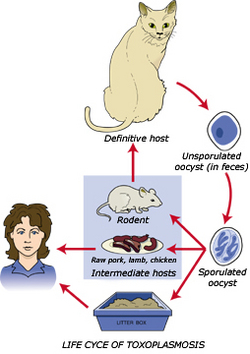
A single cell parasite known as Toxoplasma gondii is the sole cause of the infection toxoplasmosis. Toxoplasmosis is not contagious, although it can be spread through a series of events which can unfold. Cats often eat infected prey, such as birds, and then carry the Toxoplasma gondii in their system, excreting out larvae in the first few days. When another animal eats contaminated grass or plant life and is then eaten by another predator, the cycle continues until eventually those with a weakened immunity are not able to fight off the infection. Humans can contract toxoplasmosis through contact with infected cat feces, eating infected meats, using utensils that have been exposed to infected meats, drinking contaminated water, eating contaminated and unwashed fruits and vegetables, and receiving an infected organ through transplant or receiving infected blood through transfusion.
Risk factors for serious consequences related to toxoplasmosis include pregnancy, living with HIV or AIDS, having a compromised immune system for any reason, undergoing radiation or chemotherapy treatments, or the use of steroids or immunosuppressant drugs.
For most patients, there is no threat of complications related to toxoplasmosis. For patients with other medical conditions or an immune system that is significantly compromised may experience life threatening complications, including the brain infection encephalitis. Other serious complications include life threatening seizures, eye infections that lead to blindness, and hearing loss mental retardation, and blindness in children with congenital toxoplasmosis.
Most patients require no treatment when infected with toxoplasmosis. For those who require treatment, the treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the infection. Treatment options include antimalarial medications as well as antibiotics. Patients with HIV or AIDS endure similar treatments with more potent medications as well as a supplemental factor with folic acid.
Spiramycin is an antibiotic commonly used safely in pregnant women in Europe who are attempting to prevent the spread of toxoplasmosis to their child. The United States has not yet approved this antibiotic yet and it is considered an experimental medication. However, it has been used with great success throughout European countries to prevent the spread of toxoplasmosis from mother to unborn child.