Pulmonary Edema Information
Click here to scroll to the list of available medications ↓
The swelling or fluid accumulation in the lungs can cause pulmonary edema. The illness can lead to impaired gas exchange and may result in respiratory failure. The cause of pulmonary edema can be due to either the failure of the heart to remove fluid from the lung circulation or a direct injury to the lungs.
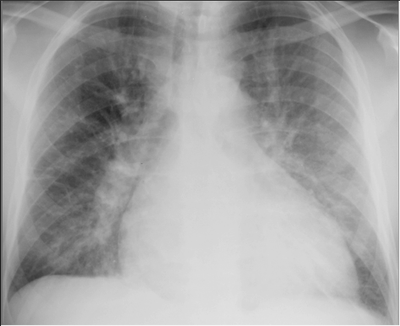
Pulmonary edema can be suspected basing from the medical history and physical examination. It can be related to a previous cardiovascular condition. The pulmonary edema can be detected through end-respiratory crackles and auscultation in the physical examination. Additionally, pulmonary edema can be predicted if there is a presence of a third heart sound. Patients with pulmonary edema would exhibit increased fluid in the alveolar walls in their X-rays.
Pulmonary edema can be caused from predetermined illnesses. Some examples are congestive heart failure, severe heart attack with left ventricular failure, severe arrhythmias, hypertensive crisis, pericardial effusion, and fluid overload either from kidney failure or intravenous therapy. Other non-cardiac illnesses that can cause pulmonary edema are inhalation of toxic gases, multiple blood transfusions, severe infection, pulmonary contusion, multiple trauma, aspiration, upper airway obstruction, reperfusion injury, and ascent to high altitude, which occasionally causes high altitude pulmonary edema.
It is possible to determine pulmonary edema if the person is having multiple problems with his or her breathing. Some of the indications of pulmonary edema include: breathing difficulty, shortness of breath, shallow breathing, rapid breathing, worsening of the shortness of breath when lying down, wheezing, restlessness, cough and dry cough and anxiety. Additionally, most pulmonary edema patients develop cyanosis, pink-stained sputum, weak or pounding pulse, swollen hands and ankles, hypotension, and enlarged or visible veins.
Always remember that pulmonary edema should be taken seriously. The doctor should be contacted when there is a feeling of light-headedness or dizziness, sweaty, or nauseated after taking a medicine. It is also advisable to monitor the weight. Gaining 2 to 3 pounds in 1 or 2 days can be a sign of pulmonary edema. It is advisable to seek care immediately if there are signs of fluid in the lungs or heart failure. Additionally, if a chest pain that spreads to the arms, jaw, or back occurs.
The first step in treating pulmonary edema is administering oxygen. The oxygen is administered through a face mask or a nasal cannula, which is a flexible tube of plastic with two openings that deliver oxygen to each nostril. These equipments are designed to ease some of the symptoms of pulmonary edema. Sometimes, it is necessary to assist the breathing of pulmonary edema patients with a machine. Medications for pulmonary edema depend on the condition and the reason of the illness. Preload reducers are used to dilate the veins the lungs and other parts of the body. This causes the decreases in fluid pressure that goes into the heart and lungs. Common preload reducers are nitroglycerin and diuretics such as furosemide. To relieve shortness of breath and anxiety, there are narcotics used. The main drug for this kind of therapy is Morphine. This has been a mainstay in treating cardiac pulmonary edema.
The afterload reducers dilate the peripheral vessels and take a pressure load from the left ventricle. Afterload reducers are available in the form of nitroprusside, enalapril, and captopril. Other doctors may also recommend aspirin. Aspirin helps to thin the blood to start smooth passage through the smaller blood vessels. Another therapeutic approach to the treatment of pulmonary edema is the use of blood pressure medications. If there is a preexisting hypertension, the doctor would recommend a medicine that would control the blood pressure. On the other hand, patients with hypotension are likely to be given drugs to raise it.
One kind of pulmonary edema is the high-altitude pulmonary edema. People experiencing HAPE during climbing or traveling at high altitudes are advised to descend a few thousand feet to relieve the symptoms. Always remember that oxygen is very helpful. In severe cases, however, researches have devised several experimental therapies. The person experiencing HAPE must be placed in an airtight bag known as hyperbaric bag. This bag is pumped with air. This stimulates the air pressure at a lower altitude. Temporary relieve will be felt from a night’s sleep in the bag. For climbers, is it possible to take the prescription medication acetazolamide. This will help treat or prevent symptoms of HAPE. Although, this drug is usually associated with side effects such as: tingling or burning in the hands, feet and mouth, confusion, diarrhea, nausea, and thirst.
When going to the hospital during a pulmonary edema scare, it is necessary to prepare oneself on what might be seen on the hospital. There are several equipments and procedures that could be used to ease the symptoms of pulmonary edema. One of these equipments include: the ventilator, ET Tube, Medicines, heart tubes/wires, chest x-ray, taking vital signs, oxygen, pulse oximeter, ECG, 12 Lead ECG, Blood Gases, Blood, and IV. After leaving the hospital, it is necessary to have a complete bed rest and sleep at least 7 hours each night and naps during the day. There are several measures that could help to reduce the risk of pulmonary edema. The first thing to consider is preventing cardiovascular disease. This is the leading cause of pulmonary edema. To reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, it is necessary to control the blood pressure. This can be done through regular exercise, eating a diet rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products, and limiting alcohol and coffee. Aside from controlling the blood pressure, it is also important to watch the blood cholesterol. Too much cholesterol can be too much of a good thing. It can cause fatty deposits in the arteries.
Other prevention tip is not to smoke cigarette. Smoking increases the risk of heart attack and lung cancer. Eating a heart-healthy diet especially one that includes fish is also advisable. Limiting salt is important since excess can trigger congestive heart failures. Managing stress and getting enough folate or folic acid is also an important prevention measure against cardiovascular diseases and pulmonary edema.