Sickle Cell Anemia Information
Click here to scroll to the list of available medications ↓
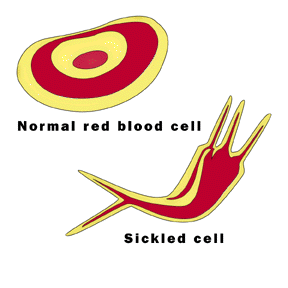
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited disease in which the normal red blood cells, which are round and move fluidly, become sickle shaped, rigid, and move through the body with stiffness and difficulty. The red blood cells which are shaped like crescents or sickles die off early, leaving a shortage of red blood cells in the body in which to carry an appropriate amount of oxygen. When sickle cells travel through the body, they have a tendency to get stuck when trying to flow through smaller blood vessels which is painful and can lead to severe complications. When the oddly shaped blood vessels become stuck, they slow blood flow to various parts of the body as well as deny the body desperately needed oxygen rich blood cells.
Having sickle cell trait means having one gene that determines the disease. Patients with sickle cell trait do not develop symptoms nor do they develop full blown sickle cell anemia. Approximately one out of every twelve African Americans has sickle cell trait. Sickle cell anemia requires two genes which determine the disease. The disease can range from mild to severe, depending on the patient. One patient may have only a few episodes in a lifetime while another patient may require repeated hospitalizations.
Symptoms vary by patient by may include anemia, period but excruciating pain, jaundice, stunted growth, frequent infections, swollen hands and feet, and vision problems. Swollen hands and feet, also known as hand-foot syndrome, is caused by the sickle cells blocking blood flow out of the hands or feet and is usually the first symptom noticed in infants. African American babies with swollen hands or feet should have their blood tested immediately. Most patients with sickle cell anemia begin to show symptoms around 4 months of age or soon after.
Sickle cell anemia is caused by a patient carrying two genes for the disease, where the gene mistakenly tells the body to make red blood cells but make it in the wrong shape. Most patients with sickle cell anemia do not have parents with sickle cell anemia, only the sickle cell trait. Those with sickle cell trait may have a small percentage of sickle cells, but not enough to cause symptoms.
The only risk factor for sickle cell anemia is having two parents with the sickle cell gene. There is no control over whether parents with sickle cell traits will have a child with sickle cell anemia.
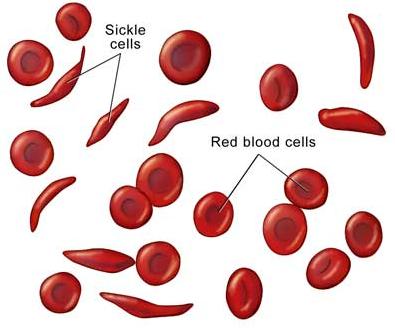
A simple blood test can diagnose sickle cell anemia. The blood cells will show up in the shape of sickles or crescents under a microscope. While it is impossible to predict how severe the disease will be for the patient, a good indicator is the concentration of sickle cells, whether the body produces a high percentage of regular red blood cells or a high percentage of sickle red blood cells. The next test that is typically performed is a blood test for anemia. Sickle cell anemia can be detected in unborn babies through a sampling of amniotic fluid. While testing in the womb is possible, treatment is not.
Serious complications may occur from sickle cell anemia, including stroke, blindness, organ damage, acute chest syndrome (a serious infection much like pneumonia but caused by trapped sickle cells in the lung’s blood vessels), gallstones, open sores, ulcers, skin infections, priapism (long, painful erections that usually require medical attention), and damage to the penis.
Bone marrow transplant is the most suitable cure for sickle cell anemia. Very few sickle cell sufferers can find a suitable donor without sickle cells. For those who are waiting for bone marrow transplants have treatment options which include antibiotics, medications to relieve pain, and a medication typically used in cancer patients known as hydroxyurea, which can simulate the production of fetal red blood cells in adults with severe sickle cell anemia.
A support system is vital in maintaining good health, whether the patient is a child or an adult. Sickle cell anemia is a lifelong disease with the chronic potential for symptoms and complications. Allowing other people to become a support system allows sufferer and parents of sufferers to stay focused on health rather than illness. Support groups can offer ideas to managing pain. Not every patient will respond to pain management techniques in the same way. Some patients will respond well while others will need a different approach. Being well informed and well supported make sickle cell sufferers more active in their own health care.