Ulcerative Colitis Information
Click here to scroll to the list of available medications ↓
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease that affects over 500,000 Americans. Ulcerative colitis causes chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, which leads to severe diarrhea, pain, and can cause life threatening complications. Ulcerative colitis often acts and appears so much like Crohn’s disease that physicians often mistake one for the other, however, Crohn’s disease affects deep layers of tissue inside the digestive tract while ulcerative colitis affects only the inner lining of the digestive tract.
There is no cure for ulcerative colitis, but therapies and medications are now making it possible for patients to experience long term remission and periods of symptom free living.
Ulcerative colitis is segregated into various types depending on its location and the symptoms. Most patients’ experiences with ulcerative colitis are unique. Ulcerative proctitis is inflammation of the rectum and some people experience only bouts of rectal bleeding. Left sided colitis is know to affect the left side and patients may experience bloody or watery diarrhea, weight loss, pain throughout the abdominal region, and cramping of the abdomen. Pancolitis affects the entire colon and may be accompanied by weight loss, severe bloody or watery diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, fatigue, and night sweats. Fulminant colitis, is rare but life threatening, and causes profuse diarrhea, severe pain, and can cause shock and dehydration. Most patients experience times of severe symptoms followed by periods of remission and relief from symptoms.

Ulcerative colitis is caused by inflammation brought about by ulcers in the intestinal tract. Ulcerative colitis tends to create on long strip of inflammation along the intestinal tract, anywhere from a few inches in length to the length of the entire intestines. While research has yet to prove one single actual cause of ulcerative colitis, research suggests that hereditary factors, a malfunction of the immune system, the overuse of antibiotics, and yet to be understood environmental factors all play a role in the causes of ulcerative colitis.
Risk factors for ulcerative colitis may include age, family history, ethnicity, and whether the patient lives in an urban and northern region. Patients living in cities in temperate climates of the United States tend to have much higher incident rates than people living in the southern states or in rural settings.
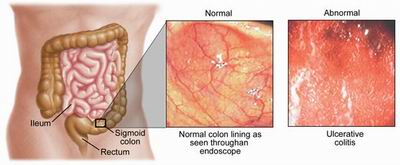
When diagnosing ulcerative colitis, the physician may need to determine a variety of factors, including the lack of another explanation for pain and diarrhea. Testing can rule out and confirm the presence of ulcerative colitis. Blood tests, colonoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, barium enemas, and small bowel x-rays can determine the presence or deny the presence of ulcerative colitis. Tests such as the flexible sigmoidoscopy allow the physician to view the colon and determine the cause of the pain and diarrhea.
Complications which may be caused by ulcerative colitis are severe and can even become life threatening. Complications may include perforated bowels, liver disease, severe dehydration, inflammation of the skin, joints, and eyes, and difficulty with pregnancy. Patients with ulcerative colitis also have a significantly increased risk of colon cancer.
Treatment option for ulcerative colitis involve attempting to relieve symptoms as well as trying to prevent flare ups and encourage long term remission. Anti-inflammatory medications and fish oil can help decrease the inflammation of the colon and provide some relief from the chronic pain and the diarrhea which can be seriously life affecting. Immunosuppressant medications often target the immune system causes and can help off set the colitis and encourage remission. Nicotine patches for smoking cessation seem to help alleviate flare ups, although no one is really sure why. Iron supplements, anti-diarrhea medications, laxatives, and pain relievers have been moderately successful in treating ulcerative colitis. New surgical procedures are offering greater hope to patients. In some cases, however surgical procedures to deal with ulcerative colitis mean removing the entire colon, which has its own set of complications.
Alternative therapies are growing in popularity, and nearly half of all sufferers of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease have turned to alternative medicines in search of successful therapies. Alternative medicines have provided a great deal of relief to the majority of those who seek relief there.